The Impact of Diabetes on Your Body: A Comprehensive Guide

Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when your blood glucose, also known as blood sugar, is too high. Over time, high blood sugar levels can cause serious health problems and affect various parts of your body. This blog will provide a detailed look at the impact of diabetes on your body, along with ways to manage it effectively.
What is Diabetes?
Diabetes occurs when your body either doesn’t produce enough insulin (a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar) or can’t use it effectively. This can lead to high blood sugar, which, if left untreated, can result in a host of complications. There are two main types of diabetes:
- Type 1 Diabetes: The body doesn’t produce insulin, and individuals must take insulin daily.
- Type 2 Diabetes: The body doesn’t use insulin well and may not make enough, leading to high blood sugar.
Immediate Impact of Diabetes on Your Body
Diabetes doesn’t just raise your blood sugar; it can have both short- and long-term effects on your body. In the early stages, symptoms might be mild and include:
- Increased thirst and frequent urination
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Slow-healing sores or cuts
These symptoms occur because the body is unable to regulate blood sugar properly, causing excess sugar to accumulate in the blood. Over time, these can worsen, leading to more severe consequences.
The Long-Term Impact of Diabetes on Your Body
Over time, poorly managed diabetes can damage many of the body’s systems. Here are the areas most affected by the impact of diabetes:
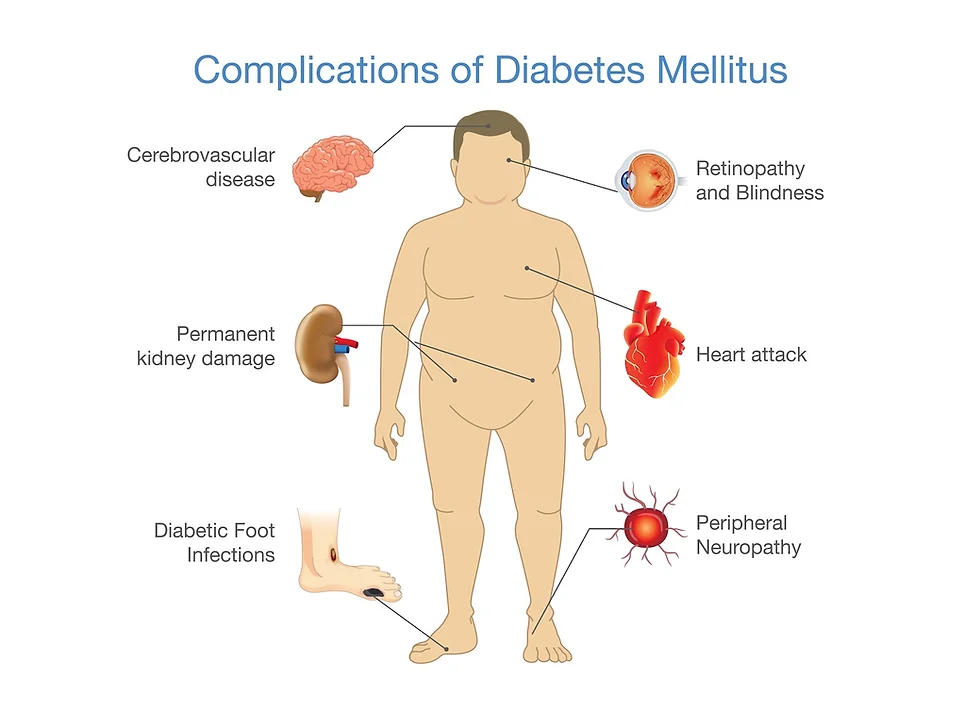
1. Heart and Blood Vessels
Diabetes significantly increases your risk of heart disease and stroke. High blood sugar can damage the blood vessels and lead to blockages, which may result in heart attacks. People with diabetes are twice as likely to suffer from heart disease compared to those without the condition. This happens because elevated glucose levels in the blood can damage the lining of blood vessels, leading to atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries).
2. Kidneys
Your kidneys filter waste from your blood, but high blood sugar can damage this filtering system. This condition, called diabetic nephropathy, can eventually lead to kidney failure if left untreated. In fact, diabetes is one of the leading causes of kidney disease.
3. Eyes
The impact of diabetes extends to your vision as well. High blood sugar can damage the blood vessels in the retina, causing diabetic retinopathy. If untreated, this can lead to blindness. Other eye-related issues include cataracts and glaucoma.
4. Nerves
Diabetes can damage nerves in your body, a condition known as diabetic neuropathy. This damage typically starts in the feet and legs, causing pain, tingling, or numbness. If left unmanaged, it can lead to infections and even amputation due to poor blood flow and the inability to feel wounds.
5. Skin and Wound Healing
Diabetes can affect your skin, making it more prone to infections and injuries. High blood sugar impairs the body’s ability to heal wounds, which is why diabetic individuals may suffer from slow-healing cuts or sores. In extreme cases, poor circulation and nerve damage can lead to amputations.
6. Digestive System
Diabetes can also affect the digestive system, leading to conditions such as gastroparesis, where the stomach takes longer to empty its contents. This can cause nausea, bloating, and poor absorption of nutrients.
Managing the Impact of Diabetes
Living with diabetes doesn’t have to mean living in fear of complications. Here are some tips to manage the condition and limit its impact on your body:
1. Regular Monitoring
Monitoring your blood sugar regularly is one of the best ways to manage diabetes. Consistently high blood sugar is the cause of most diabetes-related complications, so keeping it in check is essential.
2. Healthy Diet
Adopting a balanced diet rich in vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats is crucial for managing blood sugar. Limit processed foods and sugary snacks, as they can spike blood glucose levels.
3. Exercise
Regular physical activity helps the body use insulin more effectively, keeping blood sugar levels in a healthier range. Aim for at least 30 minutes of exercise most days of the week.
4. Medication
For many, lifestyle changes alone are not enough. Medications such as insulin or oral diabetes drugs can help maintain blood sugar within a normal range.
5. Regular Health Check-ups
Having regular health check-ups can help you stay ahead of potential complications. Blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and kidney function are especially important to monitor.
To learn more about managing diabetes and for detailed diagnostic testing, you can visit SDA Diagnostics in Meerut.
Conclusion
The impact of diabetes on your body can be severe if left untreated. From heart disease to nerve damage, the condition affects almost every organ system. However, with proper management—such as controlling blood sugar, maintaining a healthy diet, and staying active—you can live a full, healthy life despite diabetes.
Early detection and consistent monitoring are essential to prevent complications. Regular visits to your doctor and diagnostic check-ups at trusted facilities like SDA Diagnostics in Meerut can help you stay on top of your condition and ensure a healthy future.
faqs:
Diabetes can damage blood vessels and increase the risk of heart disease by causing atherosclerosis, leading to a higher chance of heart attacks and strokes.
Untreated diabetes can lead to complications like nerve damage, kidney disease, vision problems, slow wound healing, and an increased risk of infections.
Yes, managing blood sugar levels through a healthy diet, regular exercise, medications, and routine check-ups can help prevent complications of diabetes.
