Kidney Infection: Risk Factors and Prevention Tips

Kidney infection, also known as pyelonephritis, are serious bacterial infections that affect one or both of the kidneys. This infection typically begins in the bladder or urinary tract and then spreads to the kidneys. If left untreated, it can lead to severe complications, including permanent kidney damage or bloodstream infections. Understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and knowing the risk factors can help prevent kidney infections and protect your health.
What is a Kidney Infection?
A kidney infection occurs when bacteria, most commonly Escherichia coli (E. coli), enter the urinary tract and travel to the kidneys. This infection can be acute, appearing suddenly, or chronic, developing over time due to recurring infections. A kidney infection can cause various symptoms, from mild to severe, and can significantly impact your overall health if not treated promptly.
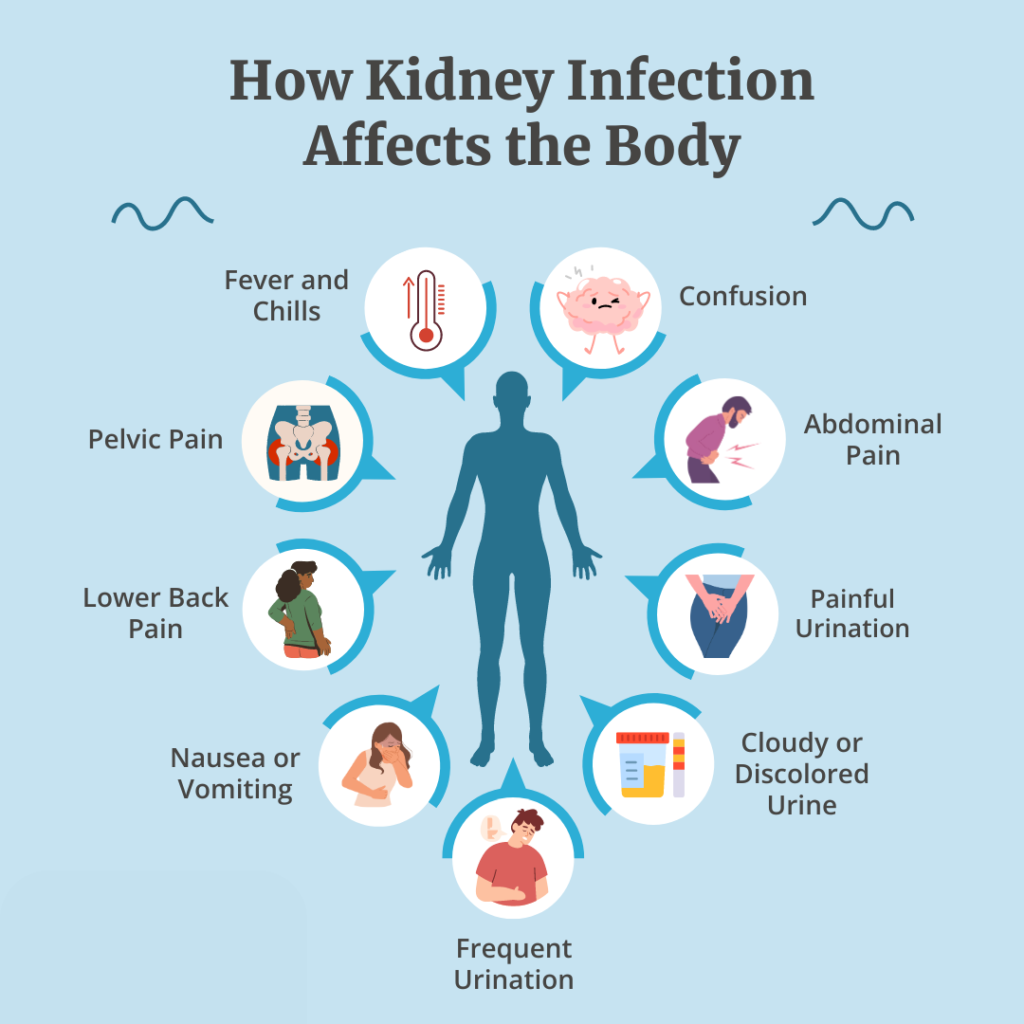
Symptoms of a Kidney Infection
Common symptoms of a kidney infection include:
- Pain or discomfort in the lower back or sides.
- A high fever or chills.
- Frequent urination or the urge to urinate, even if little urine is passed.
- Cloudy or foul-smelling urine.
- Blood in the urine.
- Fatigue and weakness.
- Nausea or vomiting.
If you experience any of these symptoms, especially alongside a urinary tract infection (UTI), it’s important to seek medical attention promptly to prevent complications.
Risk Factors for Kidney Infection
Certain factors can increase the likelihood of developing a kidney infection. These include:
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): Kidney infections often start as untreated UTIs. If a bladder infection isn’t properly treated, it can spread to the kidneys, causing a more serious issue.
Female Anatomy: Women are more prone to kidney infections due to their shorter urethra, which allows bacteria to reach the bladder more easily. Pregnancy also increases the risk of kidney infections as hormonal changes can slow urine flow.
Urinary Tract Blockages: Conditions that obstruct urine flow, such as kidney stones or an enlarged prostate, can lead to kidney infections.
Weakened Immune System: People with compromised immune systems, such as those with diabetes or HIV, are at higher risk for developing kidney infections. Certain medications that suppress the immune system can also increase this risk.
Catheter Use: Long-term use of urinary catheters can introduce bacteria into the urinary tract, leading to infections.
Vesicoureteral Reflux: This is a condition where urine flows backward from the bladder to the kidneys, increasing the risk of infection.
Prevention Tips for Kidney Infections
Preventing a kidney infection often involves taking steps to maintain a healthy urinary tract. Here are some key prevention tips:
Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps flush out bacteria from the urinary tract, lowering the risk of infection. Aim for at least 8 glasses of water daily.
Practice Good Hygiene: Women should wipe from front to back after using the toilet to prevent bacteria from the anus from entering the urethra.
Empty Your Bladder Regularly: Holding in urine can promote bacterial growth. Make sure to urinate frequently, especially after sexual activity, to reduce the risk of infection.
Avoid Irritating Products: Certain feminine products, such as douches or scented sprays, can irritate the urethra and increase the risk of infection. Opt for gentle, unscented products instead.
Take UTI Symptoms Seriously: If you suspect you have a urinary tract infection, seek treatment right away. Ignoring UTIs can lead to more serious kidney infections.
Manage Chronic Health Conditions: If you have a chronic condition like diabetes, it’s important to manage your blood sugar and overall health to prevent infections.
When to See a Doctor
If you suspect a kidney infection, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional immediately. Prompt treatment, usually with antibiotics, can prevent the infection from spreading or causing lasting damage to your kidneys. In more severe cases, hospitalization may be required to administer intravenous antibiotics and fluids.
Conclusion
Kidney infections are serious medical conditions that require immediate attention. By understanding the risk factors and following preventive measures, you can reduce the likelihood of developing an infection and protect your kidney health. Early diagnosis and treatment are key to preventing complications and maintaining a healthy urinary tract.
For accurate diagnosis and expert care, consider visiting SDA Diagnostics Meerut, where you can find the latest diagnostic services to support your kidney health and overall well-being.
faqs:
Common symptoms include lower back pain, fever, chills, frequent or painful urination, cloudy or foul-smelling urine, nausea, and fatigue.
To prevent kidney infections, stay hydrated, practice good hygiene, urinate regularly, treat UTIs promptly, and manage any chronic health conditions.
Women, people with UTIs, those with a weakened immune system, individuals using catheters, or those with urinary tract blockages like kidney stones are at higher risk.
