Cholesterol: The Good, The Bad, and The Ugly
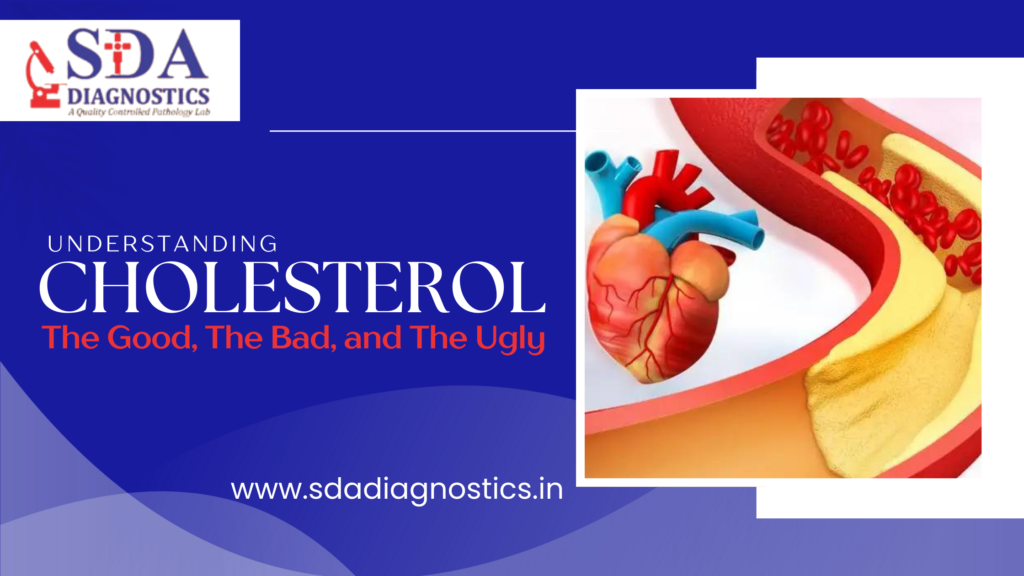
Cholesterol is a term that often sparks concern. Many people associate it with heart problems and unhealthy lifestyles. However, cholesterol itself is not entirely bad; it plays a crucial role in our body’s functioning. In this blog, we’ll explore the different types of cholesterol, their effects on our health, and how to manage cholesterol levels effectively.
What is Cholesterol?
Cholesterol is a waxy, fat-like substance found in every cell of your body. It’s essential for producing hormones, vitamin D, and substances that help you digest foods. Your liver makes all the cholesterol you need, but it is also found in some foods.
The Good: High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL)
High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL) is often referred to as “good” cholesterol. HDL helps remove other forms of cholesterol from your bloodstream. It transports low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol away from the arteries and back to the liver, where it’s broken down and eliminated from the body. High levels of HDL cholesterol can reduce the risk of heart disease and stroke.
The Bad: Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL)
Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL) is known as “bad” cholesterol. LDL cholesterol can build up on the walls of your arteries, forming plaques. These plaques can narrow the arteries, making it harder for blood to flow through. If a plaque ruptures, it can form a clot that may block blood flow, leading to heart attack or stroke. Keeping LDL cholesterol levels low is crucial for heart health.
The Ugly: Very Low-Density Lipoprotein (VLDL) and Triglycerides
Very Low-Density Lipoprotein (VLDL) and triglycerides are often grouped under “ugly” cholesterol because of their potential to cause serious health issues. VLDL carries triglycerides, another type of fat, in the blood. High levels of VLDL and triglycerides can contribute to the buildup of plaques in arteries. Triglycerides are also linked to an increased risk of heart disease, especially in people with low HDL or high LDL cholesterol levels.

How Cholesterol Affects Your Health
Having high cholesterol levels, particularly high LDL or low HDL, increases your risk of developing cardiovascular diseases. These diseases include coronary artery disease, heart attack, and stroke. Other factors that can raise your cholesterol levels include:
- Diet: Consuming saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol-rich foods can raise your cholesterol levels.
- Weight: Being overweight or obese can increase your cholesterol levels.
- Physical Activity: Lack of exercise can lower HDL cholesterol and raise LDL cholesterol.
- Age and Gender: Cholesterol levels typically rise as you age. Women usually have lower LDL levels before menopause but higher levels afterward.
- Genetics: High cholesterol can run in families.
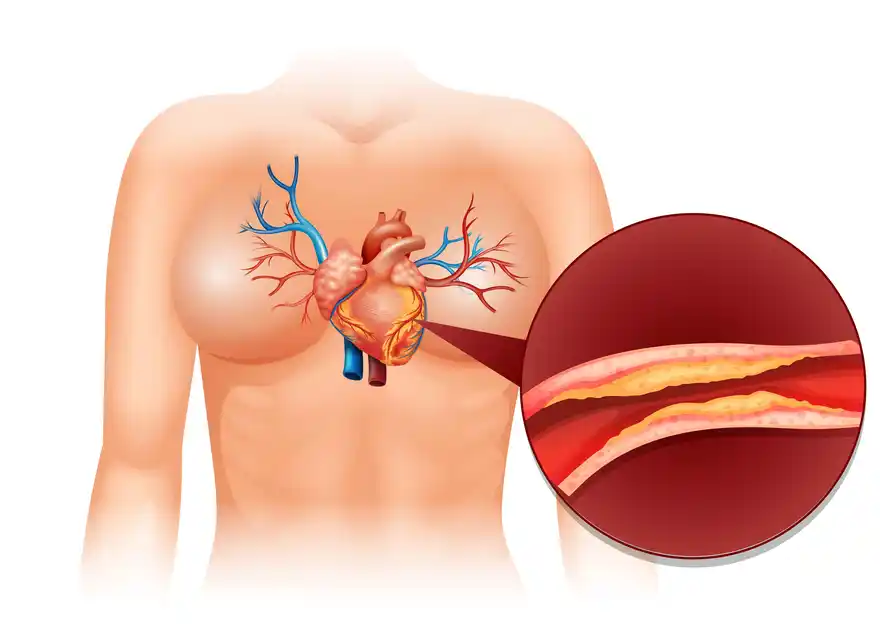
Managing Your Cholesterol Levels
Managing cholesterol involves lifestyle changes and, in some cases, medication. Here are some tips to help you maintain healthy cholesterol levels:
- Eat a Heart-Healthy Diet: Focus on a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Limit your intake of saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol.
- Exercise Regularly: Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week. Physical activity can help raise HDL cholesterol and lower LDL cholesterol.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Losing excess weight can improve your cholesterol levels and overall health.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking lowers HDL cholesterol and increases the risk of heart disease.
- Limit Alcohol: Drinking alcohol in moderation, if at all, can help manage cholesterol levels.
- Medications: If lifestyle changes aren’t enough, your doctor may prescribe medications to help lower your cholesterol.
Get Your Cholesterol Checked
Regular cholesterol screenings are essential for keeping track of your cholesterol levels and assessing your risk of heart disease. At SDA Diagnostics Meerut, we offer comprehensive cholesterol testing to help you understand your cholesterol levels and take proactive steps towards better heart health.
Conclusion
Understanding cholesterol is crucial for maintaining heart health. While HDL is the “good” cholesterol that helps remove LDL from the arteries, LDL is the “bad” cholesterol that can lead to plaque buildup and heart disease. VLDL and triglycerides add to the “ugly” side of cholesterol by increasing the risk of cardiovascular issues. By adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle and getting regular check-ups, you can manage your cholesterol levels effectively and reduce your risk of heart disease.
For more information and to schedule your cholesterol screening, visit SDA Diagnostics Meerut.
FAQS:
The main types of cholesterol are High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL), Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL), and Very Low-Density Lipoprotein (VLDL). HDL is known as “good” cholesterol because it helps remove LDL cholesterol from the bloodstream. LDL, or “bad” cholesterol, can build up in the arteries and lead to heart disease. VLDL carries triglycerides and can also contribute to artery plaque buildup. Understanding and managing these cholesterol types is essential for maintaining heart health.
It is generally recommended that adults get their cholesterol levels checked every 4 to 6 years. However, individuals with risk factors for heart disease, such as a family history of high cholesterol, smoking, high blood pressure, or diabetes, may need to have their levels checked more frequently. Consult with your healthcare provider to determine the best screening schedule for you.
Several lifestyle changes can help improve cholesterol levels, including:
- Eating a heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins while limiting saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol-rich foods.
- Engaging in regular physical activity, aiming for at least 30 minutes of exercise most days of the week.
- Maintaining a healthy weight.
- Quitting smoking, which can improve HDL cholesterol levels.
- Limiting alcohol intake. These changes, combined with regular cholesterol screenings, can significantly reduce your risk of heart disease.
